Improving quality of life through RF catheter ablation
Quality of Life Assessment with change from baseline to 3 months.
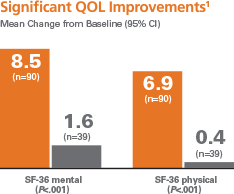
Mean quality-of-life scores at 3 months improved significantly in patients treated by RF catheter ablation compared with patients treated with AADs.1
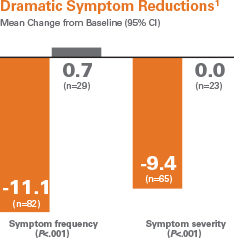
RF catheter ablation is effective in improving quality of life by eliminating arrhythmia-related symptoms such as palpitations, fatigue, and effort intolerance.2
1. Wilber DJ, Pappone C, Neuzil P, et al. Comparison of antiarrhythmic drug therapy and radiofrequency catheter ablation in patients with paroxysmal atrial
fibrillation: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2010;303(4):333-340.
2. Calkins H, Kuck KH, Cappato R, et al. 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert consensus statement
on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions,
endpoints, and research trial design: a report of the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) Task Force on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. Developed in
partnership with the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA), a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Cardiac Arrhythmia
Society (ECAS); and in collaboration with the American College of Cardiology (ACC), American Heart Association (AHA), the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS),
and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS). Endorsed by the governing bodies of the American College of Cardiology Foundation, the American Heart Association, the
European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society, the European Heart Rhythm Association, the Society of Thoracic Surgeons, the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society, and the Heart
Rhythm Society. Heart Rhythm. 2012;9(4):632-693. e21.